System Operations
In this section we describe the AIR constraints for Miden VM system operations.
NOOP
The NOOP operation advances the cycle counter but does not change the state of the operand stack (i.e., the depth of the stack and the values on the stack remain the same).
The NOOP operation does not impose any constraints besides the ones needed to ensure that the entire state of the stack is copied over. This constraint looks like so:
EMIT
The EMIT operation interrupts execution for a single cycle and hands control to the host. During this interruption, the host can read the current state of the execution and modify the advice provider as it sees fit. From the VM's perspective, this operation has exactly the same semantics as NOOP - the operand stack remains completely unchanged.
By convention, the top element of the stack is used to encode an event ID (see the events documentation for details on event structure and usage). The host can use this event ID to determine what actions to take during the execution interruption.
ASSERT
The ASSERT operation pops an element off the stack and checks if the popped element is equal to . If the element is not equal to , program execution fails.
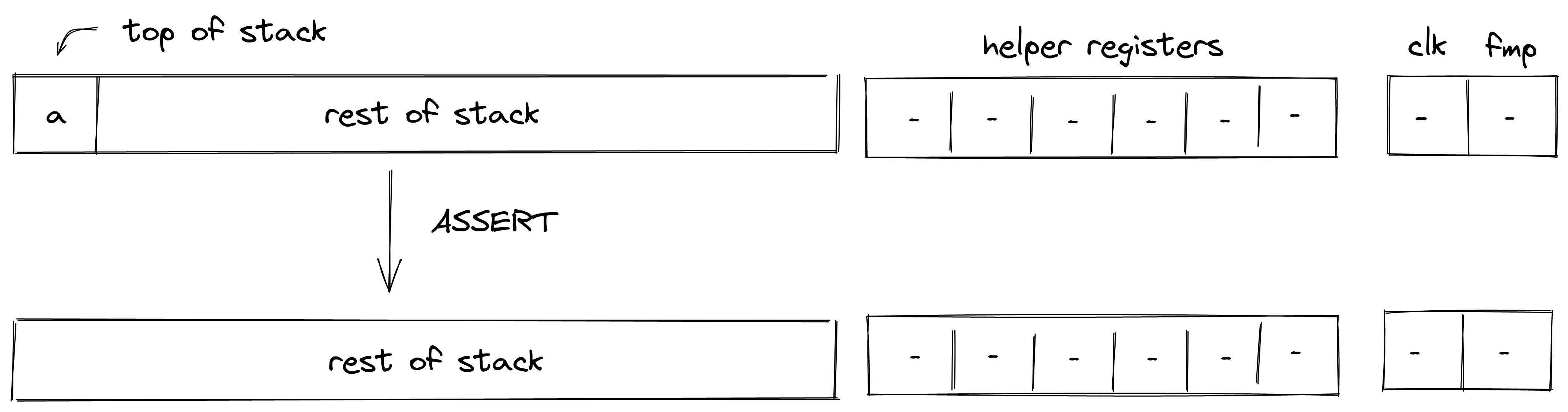
Stack transition for this operation must satisfy the following constraints:
The effect on the rest of the stack is:
- Left shift starting from position .
FMPADD
The FMPADD operation pops an element off the stack, adds the current value of the fmp register to it, and pushes the result back onto the stack. The diagram below illustrates this graphically.
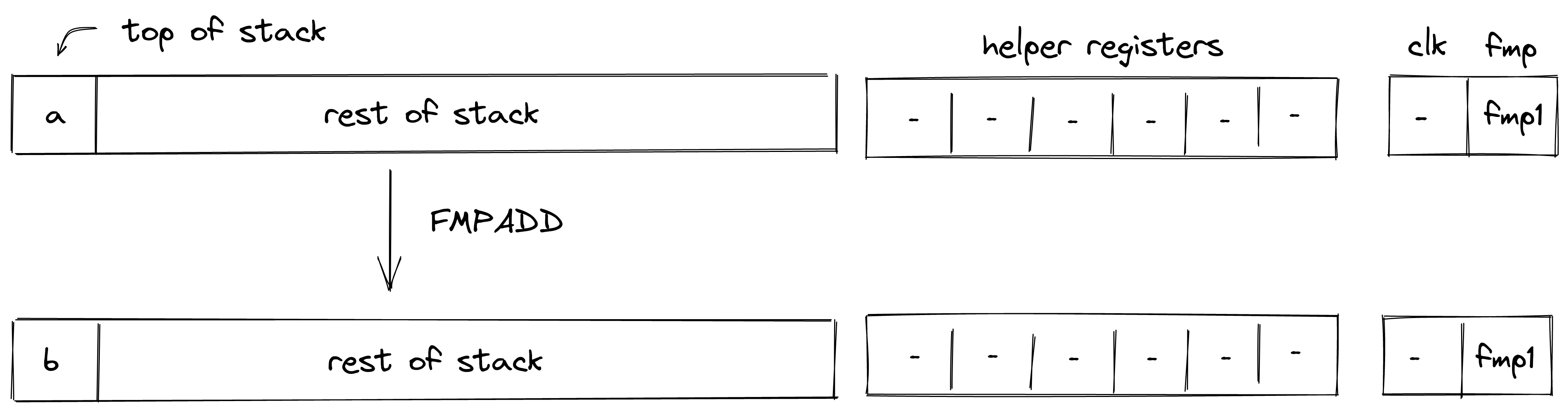
Stack transition for this operation must satisfy the following constraints:
The effect on the rest of the stack is:
- No change starting from position .
FMPUPDATE
The FMPUPDATE operation pops an element off the stack and adds it to the current value of the fmp register. The diagram below illustrates this graphically.
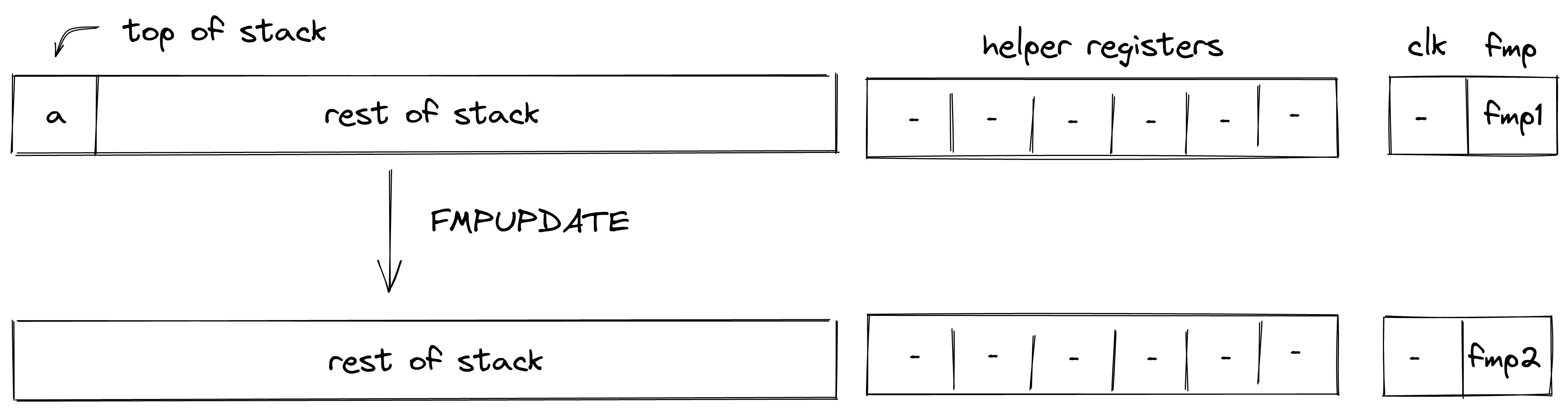
The stack transition for this operation must follow the following constraint:
The effect on the rest of the stack is:
- Left shift starting from position .
CLK
The CLK operation pushes the current value of the clock cycle onto the stack. The diagram below illustrates this graphically.
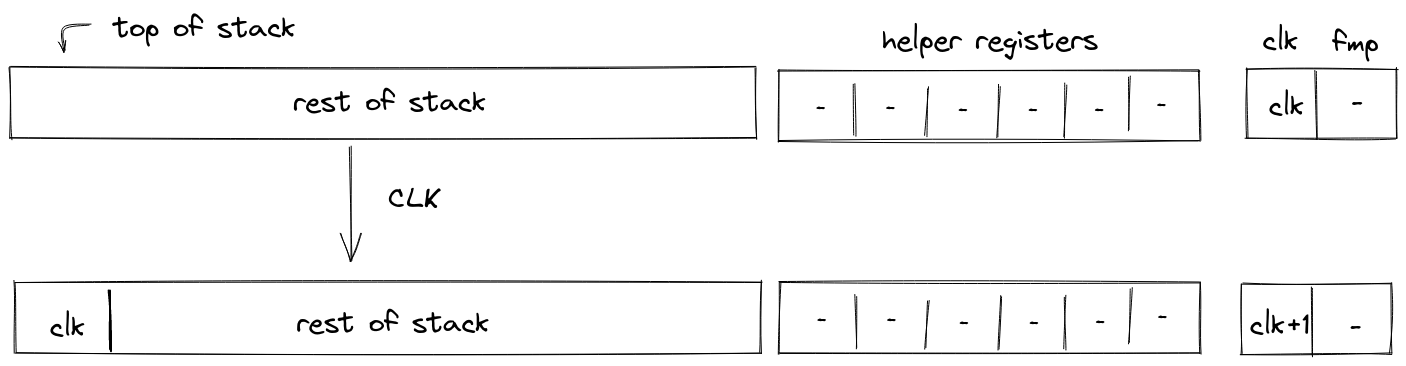
The stack transition for this operation must follow the following constraint:
The effect on the rest of the stack is:
- Right shift starting from position .